Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel
代码地址:https://github.com/wicksonZhang/Spring-Cloud-Alibaba
1. 基础概念
1.1. Sentinel 解决了什么问题?
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel 主要解决了服务与服务之间的熔断和限流,提高系统的 稳定性 和 可靠性,确保在异常情况下系统可以正常使用,同时防止故障扩散,以下是一个具体的应用场景说明:
假设有一个微服务架构的电子商务系统,其中包含多个服务,如用户服务、订单服务、支付服务等。在高并发情况下,如果某个服务出现异常或者因为流量过大而无法正常处理请求,这可能导致整个系统的崩溃或性能下降。
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel 可以通过设置每个服务的流量阈值,当达到了服务的设定的阈值之后,直接进行流量控制,防止服务过载。
1.2. Sentinel 是什么?
官网地址:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/
Github地址:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel是一个用于流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等功能的分布式系统的开源框架。它是Alibaba开发的一个子项目,与Spring Cloud无缝集成。
Sentinel 主要功能如下:
- 实时监控:Sentinel 提供了实时监控的统计功能可以在提供的 Dashboard 查看每个服务的请求量、错误率、响应时间等指标。
- 规则配置: Sentinel支持通过代码或配置文件定义流量控制、熔断降级等规则,灵活适应不同场景的需求。
- 流量控制: Sentinel可以对服务进行流量控制,限制每个服务的请求流量,防止系统过载。
- 熔断降级: 当服务出现异常或错误率超过阈值时,Sentinel可以自动触发熔断机制,停止对该服务的请求,避免错误的传播。

1.3. Sentinel 对比 Hystrix
- Sentinel 是在 Hystrix 后面进行研发的,所以本质上借鉴了 Hystrix 一些优秀的点进行了进一步的开发。
| 特点 / 框架 |
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel |
Netflix Hystrix |
| 流量控制策略 |
灵活、细致化 |
相对简单 |
| 实时监控和统计 |
支持,提供实时监控功能 |
有监控功能,但较为基础 |
| 规则配置 |
灵活,支持代码或配置文件配置 |
相对简单的配置 |
| 容错能力 |
强大的熔断降级机制 |
相对较为简单的容错机制 |
| 轻量级 |
相对较轻量级 |
相对较重量级 |
| Spring Cloud 集成 |
原生支持Spring Cloud Alibaba |
通过Spring Cloud Netflix集成 |
| 社区活跃度 |
活跃 |
项目处于维护模式 |
2. Sentinel 安装启动
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| E:\JavaProjects\Spring-Cloud-Alibaba\doc\03-Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel>java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.7.0.jar
INFO: log output type is: file
INFO: log charset is: utf-8
INFO: log base dir is: C:\Users\minuo-java02\logs\csp\
INFO: log name use pid is: false
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.0.5.RELEASE)
...............
|

3. Sentinel 具体操作
3.1. 实现需求
1
| 搭建 Sentinel 微服务项目,配合 Sentinel Dashboard 结合使用。当访问对应的控制链路时,在控制台中出现对应的监控信息。
|
3.2. 实现结果

3.3. 实现步骤
1
2
3
4
5
| 1. 创建 sentinel 服务:03-spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-server-2400
2. 导入 pom.xml 依赖
3. 创建 application.yml 依赖
4. 创建 SpringCloudAlibabaSentinelApplication 启动类
5. 创建 SentinelController 控制类
|
3.3.1. 创建 sentinel 服务
- 创建 sentinel 服务名称:03-spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-server-2400
3.3.2. 导入 pom.xml 依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.wickson.cloud.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>01-spring-cloud-alibaba-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
3.3.3. 创建 application.yml 依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| server:
port: 2400
spring:
application:
name: spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-server
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.10.20:8001
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
port: 8719
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
|
3.3.4. 创建启动类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringCloudAlibabaSentinelApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudAlibabaSentinelApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
3.3.5. 创建控制类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
@Slf4j
@Validated
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/sentinel")
public class SentinelController {
@GetMapping("/service1")
public ResultUtil service1() {
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelController.service1()");
}
@GetMapping("/service2")
public ResultUtil service2() {
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelController.service2()");
}
}
|
4. Sentinel 流量控制
在Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel中,流控规则用于定义对服务的流量控制策略。在下图中针对某一个接口进行流量控制的配置:

如下是文字版描述
- 资源名:唯一名称,默认请求路径;
- 针对来源:Sentinel 可以针对调用者进行限流,填写微服务名,指定对哪个微服务进行限流 ,默认
default(不区分来源,全部限制);
阈值类型 / 单机阈值:
- QPS:每秒钟的请求数量,当调用接口的QPS达到阈值的时候,进行限流;
- 线程数:当调用接口的线程数达到阈值的时候,进行限流;
是否集群:不需要集群
- 流控模式:
- 直接:接口达到限流条件时,直接限流;
- 关联:当关联的资源达到阈值时,就限流自己;
- 链路:只记录指定链路上的流量 (指定资源从入口资源进来的流量,如果达到阈值,就进行限流)【api 级别的针对来源】;
- 流控效果:
- 快速失败:直接失败,抛异常;
- Warm Up:根据codeFactor(冷加载因子,默认为3)的值,即请求 QPS 从阈值 / codeFactor,经过预热时长,逐渐升至设定的QPS阈值;
- 排队等待:匀速排队,让请求以匀速的速度通过,阈值类型必须设置为QPS,否则无效;
4.1. QPS-直接-快速失败
QPS-直接-快速失败:当访问接口 /sentinel/service1 当每秒钟的请求流量大于 1 之后直接快速失败
- 阈值类型:QPS
- 流控模式:直接
- 流控效果:快速失败



4.2. 线程数-直接-快速失败
线程数-直接-快速失败:当访问接口 /sentinel/service1 当每秒钟的请求线程数大于 1 之后直接快速失败
- 阈值类型:QPS
- 流控模式:直接
- 流控效果:快速失败


测试结果
1
2
3
4
5
| @GetMapping("/service1")
public ResultUtil service1() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelController.service1()");
}
|

4.3. QPS-关联-快速失败
QPS-关联 -快速失败 :当访问关联资源 /sentinel/service2 当每秒钟的请求线程数大于 1 时,直接限流 sentinel 的访问地址。
- 阈值类型:QPS
- 流控模式:关联
- 流控效果:快速失败

- 测试结果,当
/sentinel/service2 请求数大于 1 时,再请求 /sentinel/service1 会直接报错

4.4. QPS-直接-Warm Up
QPS-直接 -Warm Up :避免低水位服务器突然接收到大量请求宕机采用逐渐放宽限流策略,例如 QPS = 3,预热时长 = 10,冷加载因子默认为 3,就是要让该资源在第 10 秒的时候每秒能够承受每秒 3 次并发请求数量,第一次进行限流的时间点大概在 10/3 次请求时发生
- 阈值类型:QPS
- 流控模式:直接
- 流控效果:Warm Up

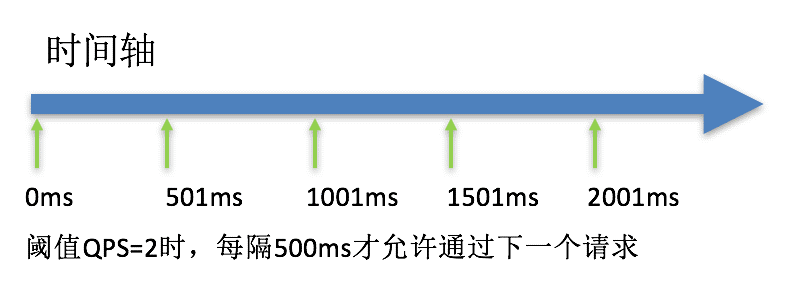
4.5. QPS-直接-排队等待
QPS-直接-排队等待:匀速器模式,所有请求堆积在入口处等待,以QPS为准每秒放行响应的请求进行处理,请求间隔为(1/阈值s),可设置超时时间来过滤掉部分等待中的请求,超时时间需要小于请求的间隔才能生效。
- 阈值类型:QPS
- 流控模式:直接
- 流控效果:排队等待

- 测试结果: 不管每秒有多少请求,只允许有一个请求通过。

4.6. 自定义限流配置
- 由于上诉中所有抛出的异常都是 Sentinel 自带异常
Blocked by Sentinel(flow limiting) ,我们需要自定义抛出异常信息。
4.6.1. 实现需求
1
2
3
4
| 1. Step-1:创建自定义限流控制类:SentinelCustomerController
2. Step-2:创建自定义限流处理类:SentinelBlockHandle
3. Step-3:创建 Sentinel 界面配置: 资源名称限流、URL 地址限流
4. Step-4:单元测试: 资源名称限流、URL 地址限流
|
4.6.2. 实现结果
- 使用 资源名称限流 测试,最后的打印结果是自定义信息。

- 使用 URL 地址限流 测试,最后的打印结果是
Sentinel 自带的异常信息。

4.6.3. 代码截图

4.6.4. 实现步骤
1
2
3
| 1. Step-1:创建自定义限流控制类:SentinelCustomerController
2. Step-2:创建自定义限流处理类:SentinelBlockHandle
3. Step-3:创建 Sentinel 界面配置
|
Step-1:创建自定义限流控制类:SentinelCustomerController
- @SentinelResource:用于定义资源,并提供可选的异常处理和 fallback 配置项
- value:资源名称
- blockHandlerClass:对应的类的 Class 对象
- blockHandler:blockHandler 对应处理 BlockException 的函数名称
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/sentinel")
public class SentinelCustomerController {
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler")
@SentinelResource(value = "customerBlockHandler", blockHandlerClass = SentinelExceptionHandler.class, blockHandler = "handleException")
public ResultUtil customerBlockHandler() {
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelCustomerController customerBlockHandler()");
}
}
|
Step-2:创建自定义限流处理类:SentinelBlockHandle
- 切记:在调用端和全局异常类中的方法名,已经方法参数一定要保持一致。不然无法限流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
public class SentinelExceptionHandler {
public static ResultUtil handleException(BlockException exception) {
ResultUtil resultUtil = new ResultUtil();
try {
if (exception instanceof FlowException) {
resultUtil = ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SENTINEL_INTERFACE_CURRENT_LIMIT);
}
if (exception instanceof DegradeException) {
resultUtil = ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SENTINEL_SERVICE_DOWNGRADE);
}
if (exception instanceof ParamFlowException) {
resultUtil = ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SENTINEL_HOTSPOT_PARAMETER_CURRENT_LIMIT);
}
if (exception instanceof SystemBlockException) {
resultUtil = ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SENTINEL_TRIGGER_SYSTEM_PROTECTION_RULES);
}
if (exception instanceof AuthorityException) {
resultUtil = ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SENTINEL_AUTHORIZATION_RULES_FAILED);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SENTINEL_INTERFACE_CURRENT_LIMIT);
}
return resultUtil;
}
}
|
Step-3:创建 Sentinel 界面配置
在 Sentinel 控制台界面中,存在两种不同的限流方式,分别是 资源名称限流 和 URL 地址限流
- 资源名称限流:资源名称是通过在
@SentinelResource 注解中指定的。
- URL 地址限流:限流规则会根据请求的 URL 进行匹配。
- 注意:使用 URL 地址限流 会抛出 Sentinel 自带异常
Blocked by Sentinel(flow limiting) ,使用 资源名称限流 则会走自定义的异常。

- 使用 资源名称限流 配置 Sentinel 界面信息

- 使用 URL 地址限流 配置 Sentinel 界面信息

5. Sentinel 熔断降级
官网地址:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/circuit-breaking.html
服务降级:当依赖服务不可用时,返回一个备用的默认值或者执行备选方案,确保系统的基本功能仍然可以使用。
例如,支付的时候,可能需要远程调用银联提供的 API;然而,这个被依赖服务的稳定性是不能保证的。如果依赖的服务出现了不稳定的情况,请求的响应时间变长,那么调用服务的方法的响应时间也会变长,线程会产生堆积,最终可能耗尽业务自身的线程池,服务本身也变得不可用。

5.1. 服务降级策略
在 Sentinel 中,降级策略是一种应对系统负载过大或异常情况的手段,通过限制或拒绝一定比例的请求,以保护系统的稳定性和可靠性。
- 慢调用比例(Slow Request Ratio): 指的是在一定时间内,系统处理时间超过预设阈值的请求所占的比例。
- 异常比例(Error Request Ratio): 表示系统在一定时间内发生异常的请求所占的比例。异常可以包括各种错误,如超时、网络错误等。
- 异常数(Error Request Number):是在一定时间内发生的异常请求的数量。

5.1.1. 慢调用比例(Slow Request Ratio)
慢调用比例(Slow Request Ratio): 指的是在一定时间内,系统处理时间超过预设阈值的请求所占的比例。
- 配置类容:我们希望每个请求在 200 ms 处理完成,如果在 200 ms 没有处理完成,我们希望在未来的 2S 中的时间窗口期打开断路器。

1
2
3
4
5
| @GetMapping("/service3")
public ResultUtil service3() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelController.service3() Slow Request Ratio");
}
|
- 测试配置:可以明显的看到当熔断之后,再次访问直接返回错误信息

5.1.2. 异常比例(Error Request Ratio)
异常比例(Error Request Ratio): 表示系统在一定时间内发生异常的请求所占的比例。异常可以包括各种错误,如超时、网络错误等。
- 配置内容:我们希望当请求数量(默认为5)的异常比例大于 80%,我们希望在未来的 3S 中的时间窗口期打开断路器。

1
2
3
4
| @GetMapping("/service4")
public ResultUtil service4() {
throw new ArithmeticException("/ by zero");
}
|
- 测试结果:我们请求的是一个错误页面,但是当请求五次之后,异常比例达到了 80% 直接熔断了服务。

5.1.3. 异常数(Error Request Number)
异常数(Error Request Number): 是在一定时间内发生的异常请求的数量。
- 配置内容:是指当资源近1分钟的异常数目超过阈值 8 之后会进行熔断,注意由于统计时间窗口是分钟级别的,若时间窗口小于 60s,则结束熔断状态后仍可能再进入熔断状态

- 测试结果:我们请求的是一个错误页面,但是当请求 9 次之后,异常数达到了 8 次直接熔断了服务。

5.2. 服务熔断
5.2.1. 实现需求
1
2
3
4
| 1. Step-1:创建消费者 03-spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-consumer-2500
2. Step-2:创建生产者 03-spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-producer2-2600
3. Step-3:创建生产者 03-spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-producer3-2700
4. 通过访问消费者然后从生产者获取对应的消息进行返回
|
5.2.2. 实现结果
5.2.2.1. Ribbon 实现结果
- 不进行任何 Sentinel 限流、降级配置,当出现业务异常时进行降级处理

- 配置 Sentinel 限流操作时, 正常情况下QPS每秒超过1S时进行限流,出现异常情况下,限流和降级同时出现。


5.2.2.2. OpenFeign 实现结果
- 测试服务降级:关闭生产者 producer1、producer2 的服务
- 测试流量控制:在 Sentinel 中配置流控规则


5.2.3. 代码截图

5.2.4. Ribbon 实现
@SentinelResource
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @SentinelResource(
value = "fallback", // 资源限定名
fallback = "handlerFallback", // fallback: 降级时调用;
blockHandler = "blockHandler", // blockHandler: 流控时调用;
exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalArgumentException.class} // 忽略异常信息
)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
@Slf4j
@Validated
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/ribbon/consumer")
public class RibbonConsumerController {
@Value("${service-url.sentinel-producer-service}")
private String serviceUrl;
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler")
public ResultUtil fallback(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
ResultUtil result = restTemplate.getForObject(serviceUrl + "/producer/" + id, ResultUtil.class);
if (result == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Id is not found");
}
if (null == result.getData()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("param is not found");
}
return result;
}
public ResultUtil handlerFallback(Long id, Throwable throwable) {
return ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SYSTEM_ERROR, "id: " + id + " ,fallback: 降级时调用, " + throwable.getMessage());
}
public ResultUtil blockHandler(Long id, BlockException blockException) {
return ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SYSTEM_ERROR, "id: " + id + " ,blockHandler: 流控时调用, " + blockException.getMessage());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| @Slf4j
@Validated
@RestController
public class Producer1Controller {
@GetMapping("/producer/{id}")
public ResultUtil producer1(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
Map<Long, String> map = this.getResult();
return ResultUtil.success(map.get(id));
}
private Map<Long, String> getResult() {
Map<Long, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1L, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
map.put(2L, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
map.put(3L, UUID.randomUUID().toString());
return map;
}
}
|
5.2.5. OpenFeign 实现
- 注意:使用
OpenFeign 本质上还是和 Ribbon 有区别的
实现步骤
1
2
3
4
| 1. Step-1: 开启消费者启动类 Sentinel 限流控制注解
2. Step-2: 配置消费者 application.yml 中 feign 对 Sentinel 的支持
3. Step-3: 创建消费者控制类 FeignConsumerController
4. Step-4: 创建消费者 Feign 调用类 ApiProducerFeign、ProducerFallback
|
Step-1: 开启启动类 Sentinel 限流控制注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringCloudAlibabaSentinelConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudAlibabaSentinelConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
Step-2: 配置 application.yml 中 feign 对 Sentinel 的支持
1
2
3
4
|
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
|
Step-3: 创建消费者控制类 FeignConsumerController
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Slf4j
@Validated
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/feign/consumer")
public class FeignConsumerController {
@Resource
private ApiProducerFeign producerFeign;
@GetMapping("/fallback/{id}")
public ResultUtil fallback(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return producerFeign.producer(id);
}
}
|
Step-4: 创建消费者 Feign 调用类 ApiProducerFeign、ProducerFallback
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Component
@FeignClient(value = "spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-producer", fallback = ProducerFallback.class)
public interface ApiProducerFeign {
@GetMapping("/producer/{id}")
public ResultUtil producer(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Component
public class ProducerFallback implements ApiProducerFeign {
@Override
public ResultUtil producer(Long id) {
return ResultUtil.failure(ResultCodeEnum.SYSTEM_ERROR, "id: " + id + " ,fallback: 降级时调用");
}
}
|
6. Sentinel 热点规则
官网地址:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/parameter-flow-control.html
热点规则:热点 key 限流是一种在分布式系统中常见的限流策略,它通过对某些热点资源或关键操作进行限制,防止其请求过于频繁,以保护系统的稳定性。其中 Sentinel 主要是以 QPS 作为限流模式
- QPS 限制(Queries Per Second):对于特定的热点 key,限制每秒钟允许的请求次数。

6.1. 实现需求
1
| 当我们访问 http://localhost/sentinel/service5?param1=1 时,当参数索引 0 每秒的 QPS 阈值超过了 1 则进行限流。
|
6.2. 实现结果

6.3. 实现步骤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @GetMapping("/service5")
@SentinelResource(value = "hotKey", blockHandler = "dealHotKey")
public ResultUtil service5(@RequestParam(value = "param1",required = false) String param1) {
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelController.service5() Hot Key");
}
public ResultUtil dealHotKey(String param1, BlockException exception) {
return ResultUtil.success("This is SentinelController.service5() dealHotKey: Error");
}
|
- 我们配置
/sentinel/service5 的界面,当参数索引 0 每秒的 QPS 阈值超过了 1 则进行限流

7. Sentinel 持久化配置
- 每当我们服务重启之后,所有的配置 流控规则、降级规则、热点参数限流规则 全部都会失效,所以针对这个问题直接配合 Nacos 做到持久化。
7.1. 实现需求
1
| 当项目重启之后依旧保留 Sentinel 服务的流控规则、降级规则、热点参数限流规则配置
|
7.2. 实现结果

7.3. 实现步骤
1
2
3
4
5
| 1. Step-1: 导入消费者 pom.xml 依赖
2. Step-2: 修改消费者 application.yml 配置
3. Step-3: 创建 Nacos 配置信息
4. Step-4: 创建对应 Sentinel 控制类的方法
5. Step-5: 创建 Sentinel 流控规则配置信息
|
Step-1: 导入消费者 pom.xml 依赖
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
Step-2: 修改消费者 application.yml 配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| spring:
application:
name: spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-consumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 192.168.10.20:8001
ip: 192.168.10.221
sentinel:
eager: true
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
port: 8719
datasource:
ds1:
nacos:
server-addr: 192.168.10.20:8001
dataId: spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-consumer
groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP
data-type: json
rule_type: flow
|
Step-3: 创建 Nacos 配置信息

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| [
{
"resource": "/feign/consumer/fallback/persistence",
"limitApp": "default",
"grade": 1,
"count": 1,
"strategy": 0,
"controlBehavior": 0,
"clusterMode": false
}
]
|
Step-4: 创建对应 Sentinel 控制类的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Slf4j
@Validated
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/feign/consumer")
public class FeignConsumerController {
@GetMapping("/fallback/persistence")
public ResultUtil persistence() {
return ResultUtil.success();
}
}
|
Step-5: 创建 Sentinel 流控规则配置信息














































